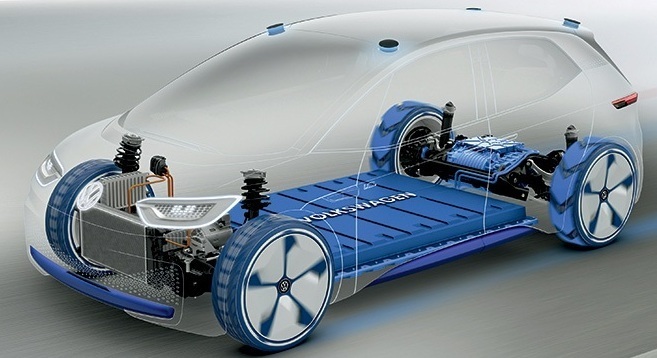
How Does An Electric Vehicle (EV) Work? An Overview of the Technology
An electric vehicle (EV) is a vehicle that uses electricity instead of gasoline or diesel fuel. EVs are propelled by an electric motor typically powered by a rechargeable battery. A charging station or regenerative braking can be used to charge the battery.
Several types of EVs are available, including all-electric vehicles (AEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). AEVs, such as the Tesla Model S and Nissan Leaf, run solely on electricity and have no internal combustion engine. PHEVs, such as the Chevrolet Volt and BMW i3, have both an electric motor and a gasoline engine.
Ree Auto advises there are several advantages over traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, including lower operating costs, emissions, and energy efficiency. They also have no tailpipe emissions, meaning no air pollution, and they are significantly cheaper to operate than gasoline-powered vehicles, as electricity is often cheaper than gasoline.
However, EVs still have challenges, such as limited driving range, lack of charging infrastructure in some areas, and limited availability of certain models.
An electric vehicle (EV) uses an electric motor, rather than an internal combustion engine, to power the car. The electric motor is powered by a rechargeable battery, which stores chemical energy and converts it into electrical energy to drive the motor.
How Does Electric Vehicle (EV) Work?
The components of an EV that make it work include:
Electric Motor
The electric motor is the heart of the EV, converting the electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to power the vehicle.
Battery
The battery is the power source for the EV, and it stores the electrical energy that powers the electric motor. Batteries can be recharged using a charging station or through regenerative braking.
Power Electronics
This electronic component system converts the battery’s electrical energy into a form that the electric motor can use. It includes components such as inverters, converters, and controllers.
Charging System
An EV can be charged using a charging station connected to the grid and uses alternating current (AC) to charge the battery. The charging system includes a charger, a power cord, and a connector that plugs into the vehicle.
Control System
The control system manages the energy flow between the battery and the electric motor, and it also controls the speed and torque of the electric motor.
A gearbox connects the vehicle’s electric motor to the wheels. The vehicle’s computer system and a power inverter control the motor’s speed by converting direct current (DC) stored in the battery to alternating current (AC) used by the motor.
The battery is charged using a charging station, which can be at home or in public, depending on availability. The battery is intended to last for a specific number of charges and discharges before it needs to be replaced.
In conclusion, electric vehicles (EVs) are a viable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, as they offer several advantages, such as lower operating costs, lower emissions, and improved energy efficiency. They work by using an electric motor, which is powered by a rechargeable battery, to power the vehicle. The battery stores electrical energy and converts it into mechanical energy to drive the motor.